India’s logistics and supply chain industry has undergone significant transformation over the past decade. From a largely fragmented and unorganized sector to an increasingly efficient and technology-driven ecosystem, the industry’s journey reflects India’s broader economic ambitions. However, while progress has been made, opportunities for further growth and optimization remain, particularly through integrating advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML).
Table of Content
A Decade Ago: An Unorganized Sector Struggling with Inefficiencies (Kal as in the Past)
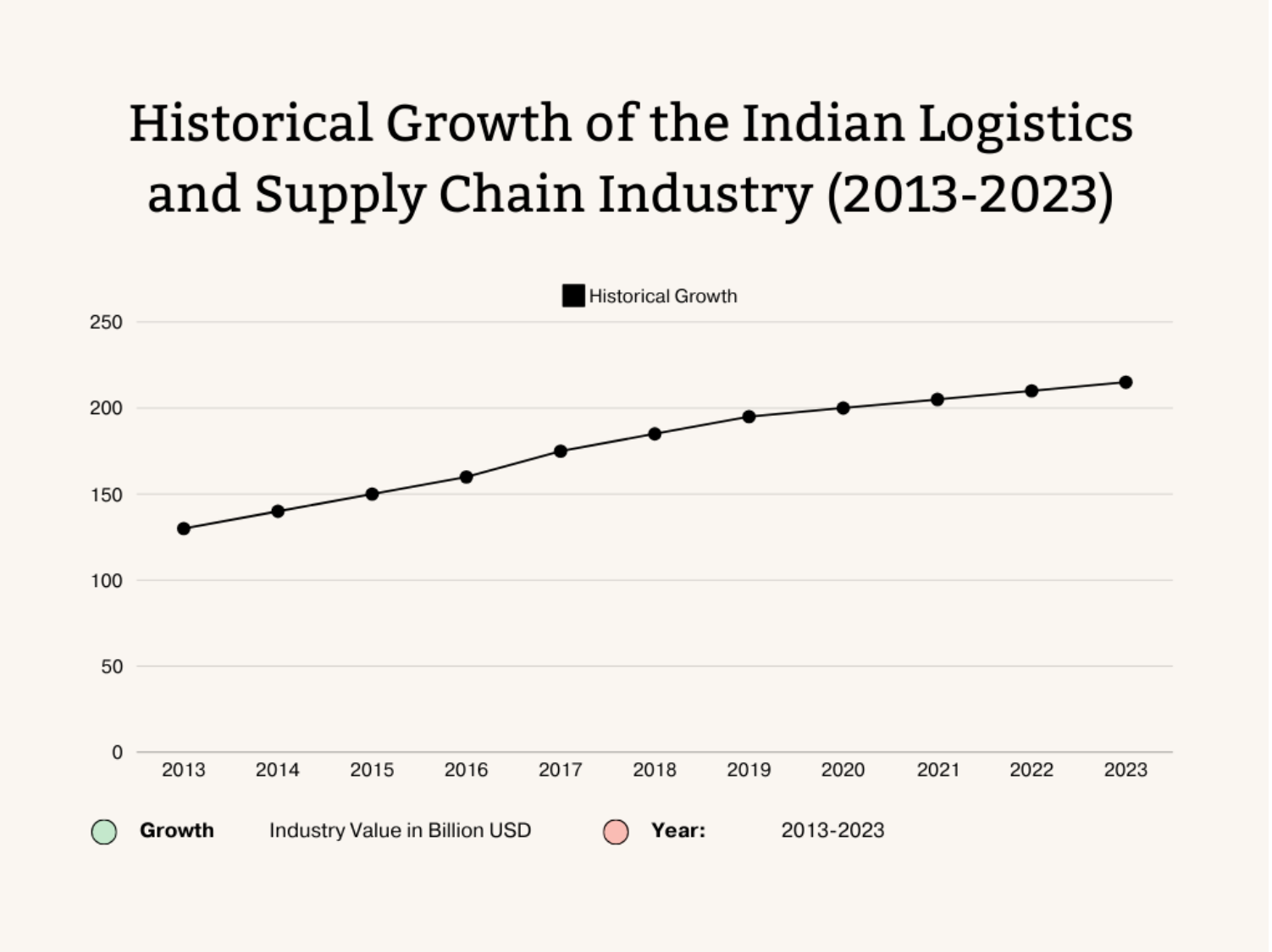
A decade ago, the logistics and supply chain industry in India was struggling with inefficiency, largely due to its fragmented nature. In 2013, the industry was valued at $130 billion but was marked by a lack of infrastructure, underdeveloped technology, and reliance on manual processes. Around 85% of the market was unorganized, with local transport companies managing the bulk of operations, leading to inefficiencies and delays.
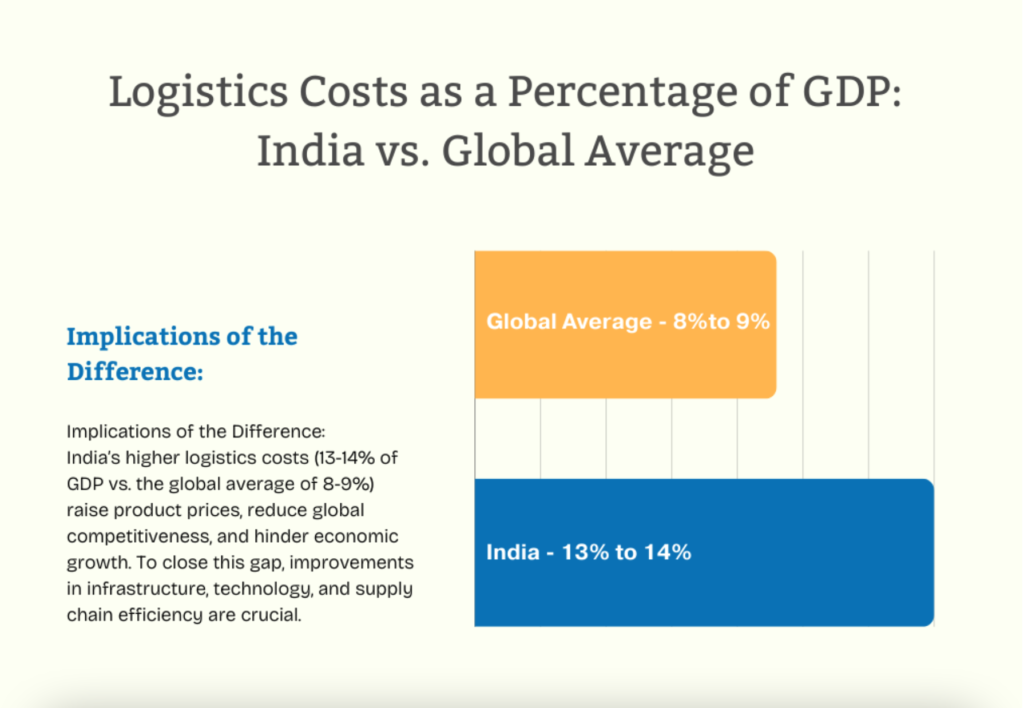
Poor road infrastructure, limited warehousing facilities, and heavy dependence on road transport (accounting for nearly 60% of cargo movement) exacerbated the issues, causing a logistics cost-to-GDP ratio of approximately 14%. This figure was significantly higher than that of developed countries like the U.S. and Germany, where logistics costs were 8-10% of GDP, impacting India’s global trade competitiveness.
Tracking shipments and managing inventory was a challenge due to minimal technology adoption. Businesses faced long delays in delivery, high transportation costs, and a lack of transparency in their supply chains. Manual systems for documentation and the complexity of India’s tax structure—pre-GST—made the interstate movement of goods a cumbersome process, further adding to the operational challenges.
Recent Changes: Government Initiatives and Digital Transformation
The past decade has seen the Indian logistics industry experience a remarkable transformation. The industry, now valued at over $215 billion as of 2023, has significantly reduced inefficiencies due to both government reforms and increased technology adoption.
- GST Implementation: The introduction of the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in 2017 marked a turning point. The GST eliminated the need for multiple interstate taxes, creating a unified national market. This significantly improved the movement of goods across state borders, reducing transit times by up to 20%.
- Infrastructure Development: The Indian government has heavily invested in infrastructure, launching programs such as the Bharatmala Project to improve road connectivity and Sagarmala to enhance port infrastructure. India has also increased its warehousing capacity from 120 million square feet in 2013 to 270 million square feet in 2023, leading to better inventory management and faster last-mile deliveries.
- Digital Adoption: Digital transformation has been a key driver of growth. The adoption of technologies such as GPS, IoT, and cloud computing has brought visibility and efficiency into the supply chain. Real-time tracking of shipments is now common, enabling companies to reduce delivery times and improve customer service. E-commerce growth further accelerated this shift, with last-mile delivery solutions evolving rapidly.
- Private Sector Innovation: Large logistics players have begun leveraging automated warehouses, drones, and robotics, optimizing operations and reducing costs. Startups in the logistics space have also contributed, offering tech-driven solutions for freight management, route optimization, and predictive maintenance.
The Future: Leveraging AI and ML for Optimization and Growth
Despite these advances, there remains significant room for improvement. Logistics costs in India still account for 13-14% of GDP, compared to the global average of 8-9%. As India aims to increase its competitiveness in the global market, leveraging AI and ML can be a crucial strategy for optimizing and scaling the logistics and supply chain industry.
- AI-Driven Demand Forecasting: AI-powered demand forecasting can help companies predict market fluctuations more accurately, leading to better inventory management and optimized warehousing. By analyzing historical data, AI can identify demand patterns and help businesses avoid overstocking or stockouts.
- Intelligent Route Optimization: AI can optimize routes for transportation, considering factors such as traffic, weather, and road conditions in real time. This not only reduces fuel consumption and delivery times but also lowers overall costs. According to industry reports, companies that have adopted AI-driven route optimization have seen a 15-20% improvement in fuel efficiency and up to 30% reduction in delivery times.
- Automated Payment Reconciliation: AI-driven payment matching and reconciliation can simplify financial transactions between logistics companies and their clients, ensuring that payments are processed more efficiently. This reduces disputes and enhances financial transparency across the supply chain.
- Predictive Maintenance and Downtime Reduction: ML algorithms can analyze data from vehicles and machinery used in the supply chain to predict potential breakdowns before they occur. This can significantly reduce downtime, increase the lifespan of assets, and save costs on repairs. For instance, predictive maintenance has been shown to reduce maintenance costs by 10-15% and equipment downtime by up to 20%.
- Smart Warehousing: AI can bring further automation to warehouses by enabling robots to efficiently pick, pack, and sort goods based on demand predictions. AI-powered systems can analyze historical trends and consumer behaviors to recommend optimal stocking levels, reducing storage costs and improving order fulfillment times.
- AI-Driven Collection and Risk Mitigation: AI can help optimize the collection process by analyzing customer behavior to identify high-risk clients. Predictive analytics can prioritize collections efforts for accounts that are most likely to delay payments, minimizing potential bad debts.
Conclusion
VP Business Operations
amlana@hutechsolutions.com
Hutech Solutions
Sources for the statistical data provided in the article:
- Indian government’s reports from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry on the logistics performance index (LPI).
- Industry reports from leading consulting firms such as KPMG, Deloitte, or PwC on the logistics and supply chain sector in India.
- The Government of India’s official reports on the impact of GST reforms on the logistics sector are available through the Ministry of Finance.
- Reports from the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) on the Bharatmala and Sagarmala projects, detailing infrastructure improvements and connectivity.
- Economic Survey of India (by the Ministry of Finance), often discusses the impact of GST on sectors including logistics.
- Data from the Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA) on warehousing facilities and capacities.
- Data from the National Institution for Transforming India (NITI Aayog) and the World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index (LPI).
- Reports from the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) and the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce & Industry (FICCI) often discuss logistics efficiency and global comparisons.
Ready to Advance your Digital Transformation?Get in touch with us.
Discover why Hutech is the right partner for your business.
MAIL US AT
sales@hutechsolutions.com
CONTACT NUMBER
+91 90351 80487
CHAT VIA WHATSAPP
+91 90351 80487
Humantech Solutions India Pvt. Ltd 163, 1st Floor, 9th Main Rd, Sector 6, HSR Layout, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560102




